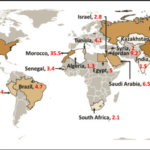
The circularity of critical minerals—encompassing recycling, reuse, and efficient resource utilization—is pivotal for India’s clean energy transition. As the nation advances towards its net-zero emissions target, the demand for minerals such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and rare earth elements, essential for technologies like electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, is surging. Implementing circular economy principles can mitigate supply chain vulnerabilities, reduce environmental impacts, and decrease reliance on imports.
Recognizing this, the Indian government has launched the National Critical Mineral Mission with a budget of ₹16,300 crore. This initiative aims to enhance self-reliance by focusing on exploration, processing, and recycling of critical minerals. By promoting recycling initiatives, the mission seeks to secure a steady supply of these essential resources, thereby supporting the nation’s green energy goals.
Industry leaders also emphasize the importance of recycling in bolstering domestic availability of critical minerals. Mines Secretary V.L. Kantha Rao highlighted that recycling efforts can significantly reduce India’s dependence on imports, ensuring a more sustainable and secure supply chain for clean energy technologies.
Furthermore, the integration of circularity in critical mineral management aligns with global best practices, fostering environmental sustainability and economic resilience. By adopting comprehensive recycling strategies, India can not only manage waste effectively but also create job opportunities and promote a circular economy that maximizes product use and minimizes waste.