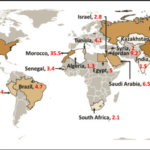
The global demand for phosphate minerals has a profound impact on both the agriculture and fertilizer industries, primarily because phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plant growth and a critical component in fertilizers. Phosphates are used to create fertilizers that improve soil fertility, boost agricultural productivity, and ensure food security worldwide. Let’s break down the effects of phosphate demand on these sectors:
Impact on Agriculture
- Key Role in Plant Growth
- Phosphorus is one of the three primary macronutrients essential for plant growth, alongside nitrogen and potassium. It is critical for energy transfer, photosynthesis, and the development of roots, flowers, and seeds.
- Phosphorus is vital for maintaining soil fertility, especially in intensive farming systems where crops are grown repeatedly on the same land. A phosphate deficiency in the soil can severely reduce crop yields, leading to lower agricultural productivity.
- Fertilizer Application
- Phosphate-based fertilizers are essential for replenishing the soil with phosphorus, which is often depleted through repeated cropping. This leads to the increased demand for phosphate rock to manufacture superphosphate, monoammonium phosphate (MAP), diammonium phosphate (DAP), and other phosphatic fertilizers.
- The use of phosphate fertilizers has helped increase crop yields dramatically over the last century, enabling global food production to keep pace with population growth. In regions where soil phosphorus levels are low, the use of phosphate fertilizers is crucial to avoid nutrient deficiencies.
- Global Food Security
- With an increasing global population (expected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050), the demand for food will continue to rise. Phosphate-based fertilizers are key to maintaining high crop yields and ensuring that food production can meet this demand.
- Fertilizer application is especially important in developing countries where farmers may not have access to other soil-improving technologies, making phosphatic fertilizers one of the most reliable ways to increase crop production.
- Impact on Sustainable Agriculture
- As the demand for phosphate increases, there is a growing concern about the sustainability of phosphate mining and its long-term availability. Phosphorus is a non-renewable resource, and the supply of high-quality phosphate rock is limited, with the majority of reserves located in just a few countries (e.g., Morocco, China, USA).
- Sustainable farming practices are being researched to reduce dependence on synthetic fertilizers, including the use of recycled phosphorus from animal manure, organic waste, and human waste, and the development of bio-based fertilizers. However, these methods are still in the early stages of implementation and may not meet the global demand for phosphorus in the short term.
Impact on the Fertilizer Industry
- Global Fertilizer Production
- The fertilizer industry is one of the largest consumers of phosphate rock, with phosphate fertilizers accounting for about 80-90% of global phosphate rock use. This makes the fertilizer industry highly sensitive to fluctuations in phosphate supply and prices.
- The production of phosphatic fertilizers involves complex chemical processes that convert phosphate rock into phosphoric acid or other forms of fertilizer. Rising demand for food has prompted continuous growth in fertilizer production capacity.
- Price Volatility
- Phosphate prices are highly volatile due to the concentration of global phosphate reserves in a few countries, geopolitical factors, and disruptions in mining and trade (e.g., strikes, natural disasters, or export restrictions).
- When demand surges—such as during periods of high crop prices or in anticipation of planting seasons—phosphate prices can spike, leading to higher costs for fertilizers. This, in turn, can impact farmers, particularly in developing countries where fertilizer costs represent a significant portion of agricultural expenses.
- Phosphate fertilizer prices are also influenced by the price of natural gas (used in the production of ammonia fertilizers) and oil prices, as these are key inputs in fertilizer manufacturing. Price increases in other fertilizer inputs can further escalate costs, creating challenges for farmers.
- Geopolitical and Trade Issues
- Phosphate-rich countries such as Morocco, China, and Russia hold significant control over global phosphate supplies, which means any geopolitical tensions or export restrictions can disrupt the supply chain.
- For example, China has occasionally imposed export bans or quotas on phosphate rock to conserve its domestic supplies, affecting global prices. Similarly, any political instability in phosphate-rich regions like Morocco could disrupt the global supply of phosphate fertilizers.
- Fertilizer companies and governments in phosphate-dependent countries may look for alternatives, including investing in domestic phosphate mining, recycling initiatives, or phosphorus recovery technologies.
- Research and Innovation in Phosphate Use
- As the supply of phosphate becomes increasingly concentrated, the fertilizer industry has been investing in technologies to improve the efficiency of phosphate use. Innovations include slow-release fertilizers, microencapsulated fertilizers, and fertilizer blends that optimize nutrient delivery.
- Researchers are also exploring ways to reduce phosphorus runoff, which causes environmental pollution, and to increase the bioavailability of phosphorus in the soil. This includes the development of more efficient fertilizers that reduce the environmental impact of over-fertilization.
- Recycling and Alternative Sources
- The phosphate fertilizer industry is also focusing on phosphorus recycling and exploring alternative sources. This includes recovering phosphorus from wastewater, livestock manure, and sewage sludge.
- Struvite, a byproduct of wastewater treatment, is being used as an alternative source of phosphorus in fertilizers. Additionally, bio-based fertilizers are gaining interest in certain markets as more sustainable alternatives to synthetic phosphate fertilizers.
Environmental and Economic Challenges
- Environmental Impact
- The widespread use of phosphate fertilizers has led to eutrophication, a process where excess phosphorus runoff enters water bodies, causing harmful algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and the destruction of aquatic ecosystems. This environmental impact has triggered calls for better phosphorus management and more sustainable agricultural practices.
- In addition to runoff, phosphate mining itself can cause land degradation and pollution from dust and heavy metals. The byproducts of phosphate processing, such as phosphogypsum (a radioactive waste), can create environmental and health concerns if not properly managed.
- Economic Access and Affordability
- The rising cost of phosphate fertilizers can limit access to essential nutrients for smallholder farmers, particularly in developing countries. This can exacerbate food insecurity and economic inequalities.
- Governments in low-income regions may subsidize fertilizer costs to support farmers, but this can strain national budgets and is not always sustainable in the long run.
- Long-Term Availability of Phosphate
- The increasing demand for phosphate minerals, combined with the finite nature of phosphate rock reserves, raises concerns about the long-term availability of this essential nutrient. Countries and industries are starting to consider strategies for phosphate conservation, such as improving fertilizer efficiency, recovering phosphorus from waste streams, and investing in alternative phosphorus sources.
- Sustainability is a growing focus within the fertilizer industry, with many stakeholders working on ways to reduce the carbon footprint of fertilizer production and increase the recycling of phosphorus in agricultural systems.
Conclusion
The global demand for phosphate minerals plays a critical role in the agriculture and fertilizer industries. Phosphorus is indispensable for maintaining soil fertility and boosting agricultural productivity, making phosphate-based fertilizers essential for global food production. However, the increasing demand for phosphate presents challenges such as price volatility, supply chain disruptions, and environmental concerns like eutrophication. The industry is evolving with innovations in fertilizer efficiency, phosphorus recycling, and sustainable farming practices to address these challenges and ensure the continued availability of this vital resource for future generations.
Hashtags
#PhosphateMinerals #FertilizerIndustry #AgricultureMinerals #PhosphateDemand #GlobalAgriculture #FertilizerProduction #SustainableFarming #FoodSecurity #PhosphateInAgriculture #PhosphateFertilizers #AgricultureSupplyChain #PhosphateResources #GlobalPhosphateSupply #FarmingInnovation #PhosphateSustainability #CropYield #SoilHealth #AgriculturalGrowth #FertilizerDemand #GlobalFarmingTrends