Water is a critical resource in mining operations, used in various stages of the process, from exploration to mineral extraction and refining. However, mining can have significant impacts on water resources, including consumption, contamination, and changes to water quality and quantity. To address these concerns, measures for water conservation and sustainable water management are implemented. Below is an overview of how water is used in mining and the strategies employed to conserve it:
How Water Is Used in Mining
- Ore Processing
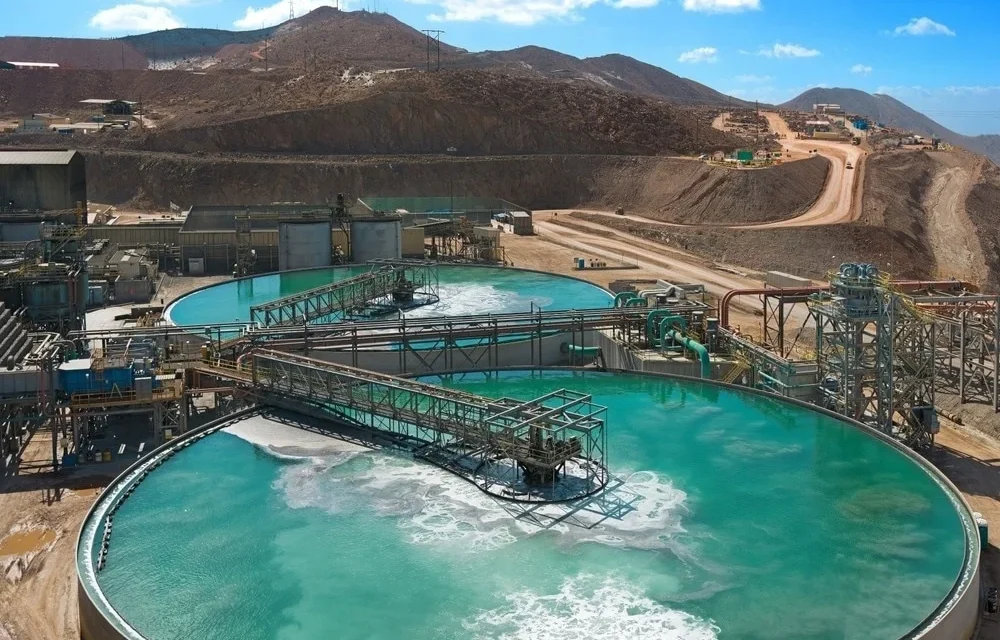
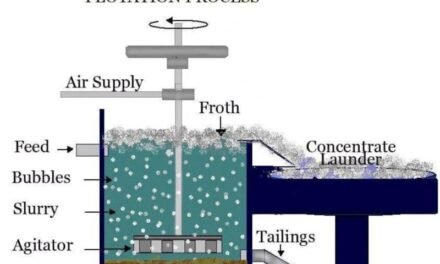
- Flotation: Water is used in flotation to create a slurry, where chemicals are added to separate valuable minerals from waste materials.
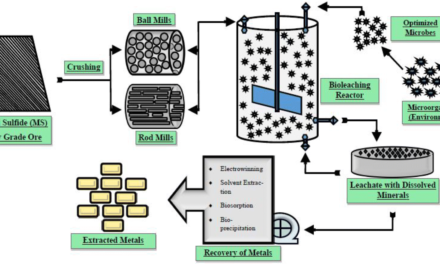
- Leaching: Water, often mixed with chemicals, is used to dissolve metals from ore (e.g., cyanide leaching for gold extraction).
- Gravity Separation: Water helps in separating minerals based on density in processes like jigs, spirals, and shaking tables.
- Thickening and Dewatering: Water is used to separate solid and liquid components in tailings and concentrate the slurry.
- Dust Suppression
- Dust Control: Water is sprayed on roads, stockpiles, and processing areas to suppress dust generated by mining operations. This helps reduce air pollution and health hazards for workers and surrounding communities.
- Cooling Systems
- Cooling Equipment: Water is often used in cooling systems to regulate the temperature of equipment like crushers, mills, and other machinery.
- Heat Exchange: Water is used in heat exchangers to absorb and dissipate heat from machinery, preventing overheating and improving efficiency.
- Transportation
- Slurry Pipelines: Water is used in slurry pipelines to transport ore particles over long distances, particularly in operations that rely on slurry transport for moving materials.
- Hydraulic Mining: In some cases, water is used to break down soft ore bodies and move the material through pipelines or directly to processing plants.
- Cyanide or Acid Leaching
- Cyanide Leaching: Water is mixed with cyanide solutions to dissolve gold and silver from ores.
- Acid Leaching: Water combined with sulfuric acid is used for extracting copper and other metals from ores, especially in heap leaching operations.
- Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking)
- Fracturing Rock: In some mining activities, especially coal bed methane or shale gas extraction, water is used in hydraulic fracturing to create fractures in rock formations and release trapped hydrocarbons.
Measures to Help in Water Conservation in Mining
- Water Recycling and Reuse
- Closed-Loop Systems: Water is reused in closed-loop systems where it is treated, purified, and recycled for continuous use in processes such as flotation, grinding, and dust suppression. This minimizes water consumption.
- Tailings Water Recovery: Water from tailings ponds is treated and reused in mining operations to reduce the need for fresh water. Technologies like filtration and reverse osmosis help in recovering clean water from tailings.
- Water Reclamation Plants: Specialized plants can treat used water from various stages of the process to make it suitable for reuse in mining operations.
- Efficient Water Use in Ore Processing
- Optimized Flotation and Leaching: By improving flotation efficiency and optimizing leaching processes, mining operations can reduce the amount of water needed for these operations.
- Thickening and Dewatering Technologies: Implementing technologies that improve the thickening and dewatering of slurries reduces the amount of water lost in tailings and maximizes the recovery of water.
- Water-Efficient Equipment
- Water-Saving Technologies: Mining companies invest in water-efficient technologies that reduce water consumption, such as low-flow nozzles for dust suppression and closed-circuit cooling systems.
- Drip Irrigation and Sprinkler Systems: For land reclamation, efficient irrigation systems are used to minimize water waste and ensure the efficient distribution of water.
- Tailings Management and Water Conservation
- Dry Stacking: Instead of using large volumes of water to store tailings in slurry form, dry stacking involves dewatering the tailings and stacking them as dry material, reducing water use and the risk of water contamination.
- Tailings Water Recovery: The recovery of water from tailings ponds is an important part of water conservation, enabling the reuse of water in other stages of mining, like processing.
- Desalination
- Alternative Water Sources: In arid regions, where fresh water is scarce, mining operations can use desalinated water from seawater for mining processes. This reduces reliance on local freshwater sources.
- Rainwater Harvesting
- Water Collection Systems: Mining operations in regions with seasonal rainfall can implement rainwater harvesting systems to capture and store rainwater, which can then be used for various purposes like dust suppression and processing.
- Use of Non-Contact Water
- Non-Contact Water Systems: Using water that does not directly interact with ore (e.g., in cooling systems) helps minimize the contamination and the need for further treatment before reuse.
- Water Conservation Policies
- Regulatory Compliance: Mining companies implement water conservation policies that comply with local, national, and international water use regulations. These policies often include water reduction targets and monitoring systems.
- Water Stewardship Programs: Many companies adopt water stewardship programs to ensure they are using water efficiently, minimizing waste, and contributing to the sustainable management of local water resources.
- Monitoring and Reporting
- Real-Time Monitoring: Using smart water meters and remote sensing technologies to monitor water usage across operations in real-time allows companies to identify inefficiencies and reduce waste.
- Transparency in Reporting: Mining companies are increasingly required to report their water use, treatment, and conservation efforts in sustainability reports, fostering accountability and encouraging further conservation.
Environmental and Social Challenges
- Water Contamination: Mining operations can result in contamination of water sources through acid mine drainage, chemical spills, or the leaching of toxic metals.
- Mitigation: Effective water treatment, containment measures (like lined ponds), and proper waste disposal help minimize contamination.
- Water Scarcity: In arid regions, mining can put pressure on already limited freshwater resources, leading to competition with local communities and agriculture.
- Mitigation: Mining companies adopt water conservation measures, such as recycling, desalination, and rainwater harvesting, to reduce their dependency on freshwater.
- Impact on Local Communities: Mining operations can affect local water availability for communities, leading to conflicts over water rights and use.
- Mitigation: Engaging with local stakeholders and communities to ensure fair water use, and using water-efficient technologies to reduce consumption, helps minimize social conflicts.
- Climate Change: Changes in rainfall patterns and increased frequency of droughts may affect water availability for mining operations.
- Mitigation: Mining companies are increasingly incorporating climate resilience strategies, including diversifying water sources and implementing adaptive water management plans.
Conclusion
Water is an essential resource in mining, used in ore processing, dust control, cooling, and transportation. However, mining can place significant pressure on local water resources, leading to environmental and social challenges. To mitigate these impacts, mining companies are adopting water conservation measures such as water recycling, efficient water use technologies, and alternative water sourcing strategies. Sustainable water management practices are crucial to ensuring that mining operations do not compromise the availability and quality of water for future generations.