The extraction of native elements like gold, silver, copper, and platinum requires specific mining techniques that are tailored to the unique properties of these elements and the deposits in which they are found. The mining methods employed can vary depending on whether the element is found in its native form (pure metal) or as part of an ore mineral. Below is an overview of the primary mining techniques used to extract these native elements:
1. Gold Mining Techniques
a. Placer Mining
- Method: This method is used to extract native gold from alluvial deposits, usually found in rivers, streams, or glacial deposits. The gold particles are often fine and mixed with other materials like sand and gravel.
- Techniques:
- Panning: Using a shallow pan, miners wash the gravel to separate the gold particles based on their high density.
- Sluicing: A sluice box uses water flow and a series of baffles to trap heavier gold particles as the lighter material is washed away.
- Dredging: Large machines (dredgers) are used to excavate and process alluvial deposits, particularly in rivers or lakes.
b. Hard Rock Mining
- Method: Hard rock mining is used when native gold is found in veins or lodes in bedrock.
- Techniques:
- Underground Mining: Miners extract ore from deep deposits using tunnels or shafts. Techniques include cut and fill mining, room and pillar mining, and sublevel stoping.
- Open-pit Mining: When gold ore is near the surface, open-pit mining involves blasting and excavating the rock to access the gold-bearing veins.
- Cyanide Leaching: Gold is often extracted from ore using cyanide leaching in which a cyanide solution dissolves the gold from the ore. This is particularly common in low-grade deposits.
2. Silver Mining Techniques
a. Placer Mining
- Method: Similar to gold, native silver can also be found in alluvial deposits and is extracted using panning or sluicing techniques.
b. Hard Rock Mining
- Method: Native silver is often found as a vein or in association with other minerals, such as lead and zinc.
- Techniques:
- Underground Mining: When native silver occurs in hard rock, miners extract it through underground mining techniques like shaft mining, drift mining, or sublevel stoping.
- Open-pit Mining: For near-surface silver deposits, open-pit mining is employed to remove the ore.
- Flotation and Smelting: After extraction, silver ore is typically processed using flotation to separate silver from other metals, followed by smelting at high temperatures to obtain pure silver.
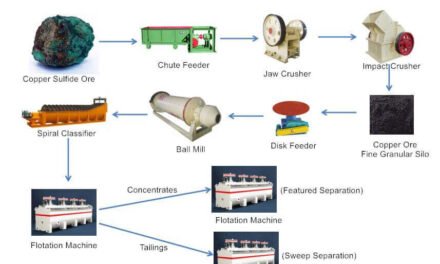
3. Copper Mining Techniques
a. Open-pit Mining
- Method: Native copper is commonly found in large deposits that are near the Earth’s surface. Open-pit mining is typically the primary method for extracting copper ore.
- Techniques:
- Blasting and Excavating: Large volumes of rock are blasted and removed to expose the copper ore. The ore is then transported to processing facilities.
- Heap Leaching: For lower-grade deposits, heap leaching is used, where the copper ore is placed in large piles and a dilute sulfuric acid solution is sprayed over the pile to dissolve the copper.
- Electrolysis: After leaching, electrolysis is used to extract copper from the solution. The copper is deposited onto a cathode, forming pure copper.
b. Underground Mining
- Method: When copper ore is too deep for open-pit mining, underground methods such as block caving or cut and fill mining are employed.
- Techniques:
- Underground Tunnels and Shafts: Miners use tunnels or shafts to access copper ore below the surface. Ore is extracted using drills, explosives, and loading machines.
- Flotation: Copper ore is often processed using froth flotation, where chemicals are added to separate the copper from waste materials.
c. Native Copper Mining
- Method: Native copper, which is found in its pure, metallic form, is typically extracted through placer mining or hard rock mining from copper-bearing veins.
- Techniques:
- Open-pit or Underground: The mining method depends on the depth of the deposit and whether it is in a vein or other formation.
4. Platinum Mining Techniques
a. Underground Mining
- Method: Platinum deposits are commonly found in ultramafic rocks, particularly in areas rich in Bushveld Igneous Complex (South Africa). These deposits are typically extracted through underground mining.
- Techniques:
- Sublevel Stoping: In platinum mines, sublevel stoping is used to extract ore from deep deposits. A tunnel is drilled into the ore body, and minerals are blasted and removed in stages.
- Room and Pillar Mining: This method involves creating tunnels through the ore body while leaving some ore intact to support the roof.
b. Open-pit Mining
- Method: For near-surface platinum deposits, open-pit mining is used to access the ore.
- Techniques:
- Blasting and Excavation: Large excavators or draglines remove the rock to expose the platinum-bearing ore.
- Froth Flotation: After extraction, the ore is processed using flotation to separate platinum from waste materials.
c. Smelting and Refining
- Method: Platinum-bearing ore is processed using smelting (at high temperatures) and refining techniques to produce pure platinum.
- Techniques:
- Electrorefining: Platinum is often refined using electrolytic refining, where impure platinum is dissolved and then re-deposited onto a cathode to form high-purity platinum.
General Processing Techniques for Native Elements
- Smelting:
- After extraction, native elements like gold, copper, and platinum are typically processed through smelting, where the metal is heated to high temperatures in a furnace to separate it from its ore and impurities.
- Refining:
- Electrorefining and chemical leaching are often used to purify the metal further. Gold and silver are often refined through the Miller process or Wohlwill process, while copper is refined using electrolysis.
- Flotation:
- In some cases, ores containing native elements are processed using flotation, where water, air, and chemicals are used to selectively separate the metal from unwanted materials.
The mining of native elements such as gold, silver, copper, and platinum requires diverse methods tailored to their specific occurrences in nature