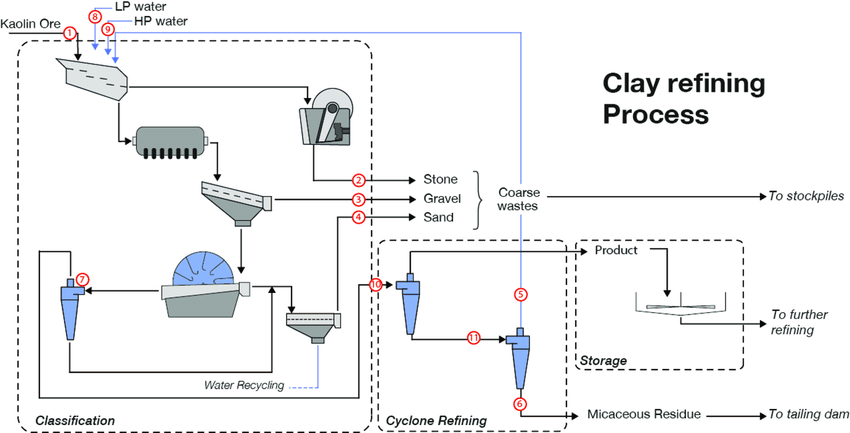
The beneficiation and refining of clay minerals are essential to enhance their quality, remove impurities, and prepare them for various industrial applications. The effectiveness of these techniques depends on the type of clay mineral being processed (e.g., kaolinite, montmorillonite, illite) and the specific impurities that need to be removed. Here are the most commonly used and effective techniques for processing clay minerals:
1. Washing and Wet Screening
Purpose: To remove soluble salts, organic matter, and fine impurities (e.g., clay fines, silts, and some iron oxide particles).
- Process: Clay is slurried in water, and mechanical methods such as hydraulic classification or vibrating screens are used to separate finer impurities from the larger, usable clay particles.
- Application: This technique is especially effective for kaolinite and montmorillonite clays, where high purity is desired for applications like ceramics, paper coating, and cosmetics.
- Effectiveness: Washing removes fine particles and some soluble contaminants, enhancing the purity of the clay. It’s a low-cost, straightforward method but may not completely remove minerals like iron oxide.
2. Air Classification and Dry Screening
Purpose: To separate coarse and fine fractions and remove lightweight impurities (such as plant material).
- Process: The clay is passed through air classifiers or air separators, where lighter impurities are blown away from the heavier clay particles. This method is commonly used after drying to separate particle sizes.
- Application: Used for kaolinite, illite, and bentonite clays to produce different particle size fractions for various applications.
- Effectiveness: Air classification is a cost-effective way to separate the finer and coarser fractions, especially when particle size is a key determinant in the clay’s commercial value.
3. Gravity Separation
Purpose: To remove heavier impurities (e.g., quartz, feldspar, and heavy metals) that have a higher density than the target clay minerals.
- Process: The clay is passed through a spiral concentrator, shaking table, or jig, where gravity is used to separate the lighter clay minerals from the denser, unwanted impurities.
- Application: Gravity separation is commonly applied to kaolinite, bentonite, and illite when the target mineral has a lower specific gravity than the impurities.
- Effectiveness: This technique is effective at removing certain types of coarse impurities, particularly in deposits with significant mineralogical variation.
4. Flotation
Purpose: To selectively separate hydrophobic impurities (such as iron oxides, carbonates, and some silicates) from the clay minerals.
- Process: The clay slurry is mixed with flotation reagents (e.g., frothers and collectors) to create foam, and air is bubbled through the mixture. Impurities that are hydrophobic attach to the bubbles and float to the surface, where they are skimmed off, leaving the clay behind.
- Application: Often used in the refining of kaolinite to remove iron oxide impurities, as iron stains reduce the quality of kaolin used in ceramics and paper production.
- Effectiveness: Flotation is highly effective for removing iron and other colored impurities from kaolinite and other clays, particularly when the goal is to produce high-quality, bright clays.
5. Chemical Leaching
Purpose: To selectively remove chemical impurities such as iron, aluminum, and calcium that affect the quality of clay minerals.
- Process: A chemical leaching agent (e.g., hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, or sodium hydroxide) is applied to the clay to dissolve unwanted impurities. The process may be followed by washing to remove the leachate.
- Application: Used primarily in kaolinite processing to remove iron oxides or in bentonite refinement to reduce magnesium or calcium content.
- Effectiveness: Leaching is highly effective for removing specific impurities that cannot be easily separated by physical methods. However, it can be costly and produce waste that must be properly managed.
6. Magnetic Separation
Purpose: To remove magnetic impurities such as iron oxides, which can discolor the clay or degrade its properties.
- Process: The clay is passed through a magnetic separator, which uses a magnetic field to attract iron particles and other magnetic impurities, leaving the non-magnetic clay behind.
- Application: Magnetic separation is commonly used to purify kaolinite and bentonite, where iron content is critical to quality.
- Effectiveness: This technique is very effective for removing iron oxides, especially when the iron is in the form of discrete particles, and it is relatively low-cost compared to other refining methods.
7. Hydraulic Classification
Purpose: To separate particles based on settling velocity or particle size, enhancing the removal of fine or coarse impurities.
- Process: Clay is suspended in water and then allowed to settle under gravity in a classifier, separating fine, light materials from coarser, heavier fractions.
- Application: Used for kaolinite and montmorillonite to remove sand, quartz, and other coarse contaminants.
- Effectiveness: This method is effective for coarse material removal and is commonly used in conjunction with other methods like washing and flotation.
8. Soda Ash Activation (for Bentonites)
Purpose: To improve the swelling capacity and adsorption properties of bentonite clays, particularly montmorillonite, by altering the chemical composition.
- Process: Bentonite is mixed with soda ash (sodium carbonate) to activate the clay, which enhances its cation exchange capacity (CEC) and makes it more effective as a drilling fluid or binder.
- Application: This technique is primarily used for bentonite processing in applications such as oil drilling, foundry sand, and environmental applications.
- Effectiveness: Soda ash activation is particularly effective for improving the swelling and adsorption properties of bentonite, making it more suitable for high-performance applications like drilling muds.
9. Calcination
Purpose: To improve the properties of certain clay minerals, particularly kaolinite, by heating them to high temperatures, which can remove water content and alter mineral structures.
- Process: The clay is heated to temperatures between 500°C and 900°C. This process is used to remove moisture and volatile impurities, and in the case of kaolin, to increase brightness and whiteness.
- Application: Used in the production of ceramic products, porcelain, and refractories, where high-quality kaolinite is needed.
- Effectiveness: Calcination improves the plasticity, strength, and whiteness of kaolin, making it suitable for premium applications like fine ceramics.
10. Ultrasonic and High-Pressure Water Treatment
Purpose: To disaggregate fine clay particles and remove fine impurities or organic material that may not be removed by standard washing or screening.
- Process: Ultrasonic waves or high-pressure water jets are used to break apart agglomerated clay particles and improve particle size distribution. This technique can also be combined with other methods such as flotation for better impurity removal.
- Application: Useful for fine clays, particularly when high purity and fine particle size are required.
- Effectiveness: Highly effective for breaking up fine agglomerates and improving the quality of ceramics and pharmaceutical clays.
Conclusion
The most effective beneficiation and refining techniques for clay minerals depend on the desired end-use application and the specific impurities present in the raw clay. Methods like washing, flotation, magnetic separation, and chemical leaching are commonly used to enhance the quality of clays like kaolinite and bentonite, while techniques like soda ash activation and calcination are tailored to specific applications such as drilling fluids and ceramics. Combining multiple methods often yields the best results, ensuring the clay is purified and optimized for its intended use.
Hashtags
#ClayMineralBeneficiation #ClayProcessing #ClayRefining #MineralRefinement #ClayPurification #ClayUpgrading #BeneficiationTechniques #ClaySeparation #FlotationProcess #SedimentationTechniques #ClayExtraction #MineralProcessingTech #ClayQualityImprovement #MineralSeparation #ClayMineralTech #SustainableMining #IndustrialMinerals #ClayInnovation #MineralResources #EcoFriendlyProcessing