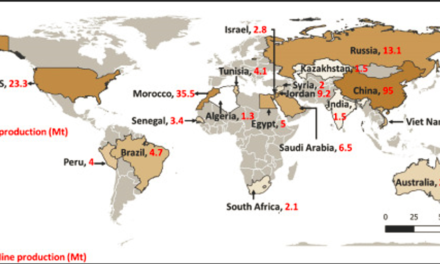
The extraction of halide minerals like halite (rock salt) and fluorite (fluorspar) depends on their geological formation, depth, and economic viability. The most common extraction methods include:
1. Halite (Rock Salt) Extraction Methods
A. Underground Room and Pillar Mining (Most Common for Rock Salt)
- Method:
- Large rooms are excavated, leaving behind “pillars” of salt to support the mine.
- Mechanical equipment like continuous miners or drills and blasting is used to extract the salt.
- Used For: Industrial salt, de-icing, and chemical production.
- Example Sites:
- Sifto Salt Mine, Canada (World’s largest underground salt mine).
- Goderich Salt Mine, USA.
B. Solution Mining (Brine Extraction)
- Method:
- Water is injected into underground salt deposits, dissolving halite.
- The brine (saltwater) is pumped to the surface and evaporated to extract pure salt.
- Used For: Table salt, industrial chemicals (chlorine, soda ash).
- Example Sites:
- Great Salt Lake, USA.
- Dead Sea, Israel & Jordan.
C. Solar Evaporation (For Salt Flats and Lakes)
- Method:
- Saltwater from oceans, lakes, or artificial ponds is evaporated using sunlight.
- The remaining salt is harvested.
- Used For: Food-grade salt, industrial salt.
- Example Sites:
- Salar de Uyuni, Bolivia.
- Salar de Atacama, Chile.
2. Fluorite (Fluorspar) Extraction Methods
A. Open-Pit Mining (For Surface Deposits)
- Method:
- Large-scale excavation of fluorite veins using drilling and blasting.
- Ore is transported to a processing plant for crushing and beneficiation.
- Used For: Metallurgy (steelmaking flux), glass and ceramics.
- Example Sites:
- Mongolia, China, South Africa (Vergenoeg Mine).
B. Underground Mining (For Deep Fluorite Deposits)
- Method:
- Shafts and tunnels are created to access high-grade fluorite veins.
- Conventional room and pillar or cut and fill mining techniques are used.
- Used For: High-purity fluorite for hydrofluoric acid, refrigerants, and aluminum processing.
- Example Sites:
- Illinois-Kentucky Fluorspar District, USA.
- Okorusu Fluorite Mine, Namibia.
C. Beneficiation and Processing
- After extraction, fluorite undergoes processing:
- Crushing & grinding to reduce ore size.
- Flotation separation to remove impurities.
- Drying and refining for marketable grades.